Overview of ESG Progress in China
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is an investment philosophy and evaluation standard that goes beyond traditional financial performance and focuses on the environmental, social, and governance effectiveness of a company. This standard aims to evaluate a company's behavior, predict its future financial performance, and measure its contribution to promoting sustainable economic development and fulfilling social responsibility. Before the rise of ESG concepts, concepts such as "ethical investment," "responsible investment," and "green finance" had already begun to emerge.
In 2006, the release of the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) supported by the United Nations laid the foundation for the development of ESG concepts. In the same year, a research report by Goldman Sachs integrated environmental, social, and governance concepts and officially proposed the ESG concept. Subsequently, ESG gradually became a new dimension for non-profit organizations, governments, and other diverse entities to observe the sustainable governance of organizations.
In 2023, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) launched the International Financial Reporting Sustainability Disclosure Standards, which is the world's first ESG reporting standard and provides a unified framework for climate and sustainability information disclosure for companies in various countries, enhancing cross-border comparability.
The ESG policy framework in China
The ESG concept coincides with China's modernization development goals, emphasizing both ecological protection and the improvement of social responsibility and governance level. From the "dual carbon" goals to rural revitalization, and then to modernization of governance, all provide rich connotations and broad space for the practice of ESG in China. To promote ESG development, the Chinese government and relevant departments have introduced a series of policies (Table 1).
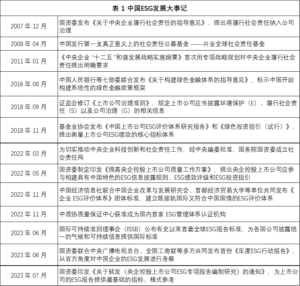
In terms of top-level design, the Chinese government explicitly requires companies to incorporate "fulfilling social responsibility" and "establishing a sound ESG system" into their internal governance. Since 2007, the State owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission has issued a series of guidance requiring central enterprises to integrate social responsibility into their development strategies, daily operations, and international operations. In 2018, the China Securities Regulatory Commission revised the "Code of Corporate Governance for Listed Companies" and added disclosure requirements on environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. Subsequently, the Fund Industry Association also released a research report on ESG evaluation system and green investment guidelines. In 2022, the State owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission proposed to explore the establishment of a sound ESG system, promote the participation of listed companies controlled by central enterprises in building ESG information disclosure rules, performance ratings, and investment guidelines with Chinese characteristics. By 2023, the State owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission requires listed companies controlled by central enterprises to achieve full coverage of ESG special report disclosure, and provides basic indicators and format references for ESG reports of listed companies.
Key links in China's ESG practice
In the practical application of ESG, information disclosure, evaluation system, and investment constitute the three core elements. The current policy mainly focuses on the standardization of information disclosure, while the evaluation system and investment aspects are relatively weak.
In terms of information disclosure, the China Securities Regulatory Commission and the two major stock exchanges (Shenzhen Stock Exchange and Shanghai Stock Exchange) have both issued detailed disclosure rules and guidelines. The China Securities Regulatory Commission encourages companies to proactively disclose their social responsibility performance, while the Shenzhen Stock Exchange and the Shanghai Stock Exchange provide specific disclosure frameworks and quantitative indicators. In addition, the two institutions will also include the disclosure of social responsibility in the assessment of information disclosure work of listed companies, ensuring the richness and completeness of the report content.
In terms of ESG evaluation system, the National Development and Reform Commission proposed to study and carry out ESG evaluation of investment projects in 2022. Subsequently, the China Economic Information Society and other units jointly released the "Corporate ESG Evaluation System" group standard that is in line with international standards and in line with China's national conditions. At the same time, some regions such as the China (Tianjin) Pilot Free Trade Zone have also released ESG evaluation index systems.
In terms of ESG investment, Chinese policies pay more attention to green finance that is closely related to it. Since 2016, China has integrated the concept of green development into G20 issues and included the construction of a green finance system in the 13th Five Year Plan. Since then, seven ministries and commissions, including the People's Bank of China, have jointly issued guidance on the green financial system, realizing the unification of green bond evaluation standards with other green financial standards in China.
Participants in China's ESG ecosystem
The ESG ecosystem in China is composed of multiple entities such as government departments, physical enterprises, asset management agencies, and ESG professional service organizations, jointly promoting the popularization and practice of ESG concepts in China.
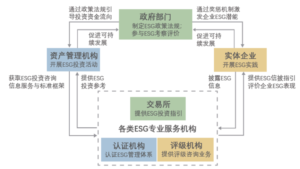
The three major stock exchanges (Shanghai Stock Exchange, Shenzhen Stock Exchange, and Beijing Stock Exchange) play a leading role in ESG practices. The Shanghai Stock Exchange focuses on the supply of ESG fund products and indices, while the Beijing Stock Exchange supports the listing and financing of innovative small and medium-sized enterprises in green and low-carbon industries. The Shenzhen Stock Exchange continues to improve its ESG information disclosure rules and promote listed companies to practice ESG concepts.
At present, there are about thirty ESG rating agencies in the Chinese capital market, among which Wind, Shangdao Ronglv, Huazheng, Jiashi Fund and other institutions have more advantages in evaluation scope, data capabilities and analysis tools. The Social Value Investment Alliance and the China Securities Investment Fund Industry Association are more focused on the social value of enterprises, and have added distinctive indicators in line with China's development goals.
