On December 16, 2024, the Ministry of Finance, together with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Ecological Environment, the Ministry of Commerce, the People's Bank of China, the State owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council and the State Administration of Financial Supervision, jointly promulgated the document numbered CK [2024] No. 17- Basic Standards for Enterprise Sustainability Reporting (Trial) (hereinafter referred to as the "Basic Standards"). This move marks the official launch of the construction of a unified sustainability reporting standard system in China, which has profound milestone value.
The Basic Principles consist of six chapters and 31 articles, with the main contents as follows:
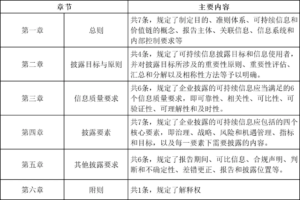
Overview of the Core Content of the Basic Principles
1、 The composition of the sustainable disclosure system for enterprises
The Basic Guidelines establish a framework for sustainable information disclosure by enterprises, which consists of three parts: basic guidelines, specific guidelines, and application guidelines. Among them, the basic principles set general disclosure requirements; Specific guidelines propose detailed disclosure standards for key areas such as environment, society, and governance; The application guide provides practical guidance for various industries and addresses difficult issues in the disclosure process by explaining and refining the content of the guidelines.
2、 The Importance of Value Chain in Sustainable Information Disclosure
The value chain encompasses the entire lifecycle activities of a company, from product design to delivery, consumption, and disposal, as well as the interactions, resources, and relationships associated with these activities. The Basic Principles emphasize that when conducting sustainable information disclosure, companies should fully consider the impact of their value chain and ensure the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the disclosed content.
3、 Consistency requirements for reporting subjects
To ensure the coherence and comparability of information, the Basic Principles require that the reporting entity for sustainable information disclosure should be consistent with the reporting entity for financial statements. At the same time, enterprises should reveal the inherent connections between sustainable information, financial statement information, and other related information, and explain them through indexes or textual explanations.
4、 The Six Dimensions of Information Quality Requirements
The Basic Principles propose six information quality requirements: reliability, relevance, comparability, verifiability, comprehensibility, and timeliness. These requirements aim to ensure that the disclosed sustainable information is truthful, useful, comparable, verifiable, easy to understand, and timely, thereby meeting the needs of information users.
5、 Four core disclosure elements
The Basic Principles specify that the sustainable information disclosed by enterprises should include four core elements: governance, strategy, risk and opportunity management, as well as indicators and goals. These four elements occupy a significant portion of the standard provisions, detailing the content and precautions that each should disclose.
6、 Other disclosure requirements
The Basic Principles also stipulate requirements for reporting periods, comparable information, compliance statements, judgments and uncertainties, error correction, and disclosure locations. Among them, the disclosure time should be consistent with the financial statements, using clear structure and language, and disclosed to the public simultaneously with the financial statements. Enterprises should also publish sustainability reports through official websites or other means, and can obtain the necessary information from other reports through cross referencing.

7、 Integration with international standards and localized innovation
The Basic Principles have been localized and innovated based on international financial reporting sustainability disclosure standards (such as IFRS S1) and combined with the actual situation in China. This institutional arrangement is not only conducive to aligning with international standards, but also fully considers the actual situation and capacity of Chinese enterprises.
8、 Implementation Strategy and Gradual Promotion
The Basic Principles adopt the implementation strategy of "distinguishing key points, piloting first, gradually progressing, and advancing step by step". In terms of implementation scope and requirements, full consideration has been given to the development stage and disclosure capability of the enterprise, avoiding a one size fits all mandatory implementation approach. Before formally defining the scope and requirements of implementation, encourage enterprises to voluntarily implement this standard.
9、 Innovation and challenges in incorporating value chain into disclosure scope
The Basic Principles pioneers the inclusion of the entire value chain in the scope of sustainable information disclosure, which requires companies to examine the impact of their business activities on the environment, society, and governance from a broader perspective. For chain owners, this means building a more complex and refined management system, and ensuring that every link in the value chain meets ESG standards; For small and medium-sized enterprises in the supply chain, they face challenges such as limited resources and a lack of professional teams. However, this innovative measure will drive the entire value chain towards a more sustainable direction.
